What's new arround internet
| Src | Date (GMT) | Titre | Description | Tags | Stories | Notes |
| 2024-03-05 19:03:47 | Rester en avance sur les acteurs de la menace à l'ère de l'IA Staying ahead of threat actors in the age of AI (lien direct) |
## Snapshot Over the last year, the speed, scale, and sophistication of attacks has increased alongside the rapid development and adoption of AI. Defenders are only beginning to recognize and apply the power of generative AI to shift the cybersecurity balance in their favor and keep ahead of adversaries. At the same time, it is also important for us to understand how AI can be potentially misused in the hands of threat actors. In collaboration with OpenAI, today we are publishing research on emerging threats in the age of AI, focusing on identified activity associated with known threat actors, including prompt-injections, attempted misuse of large language models (LLM), and fraud. Our analysis of the current use of LLM technology by threat actors revealed behaviors consistent with attackers using AI as another productivity tool on the offensive landscape. You can read OpenAI\'s blog on the research [here](https://openai.com/blog/disrupting-malicious-uses-of-ai-by-state-affiliated-threat-actors). Microsoft and OpenAI have not yet observed particularly novel or unique AI-enabled attack or abuse techniques resulting from threat actors\' usage of AI. However, Microsoft and our partners continue to study this landscape closely. The objective of Microsoft\'s partnership with OpenAI, including the release of this research, is to ensure the safe and responsible use of AI technologies like ChatGPT, upholding the highest standards of ethical application to protect the community from potential misuse. As part of this commitment, we have taken measures to disrupt assets and accounts associated with threat actors, improve the protection of OpenAI LLM technology and users from attack or abuse, and shape the guardrails and safety mechanisms around our models. In addition, we are also deeply committed to using generative AI to disrupt threat actors and leverage the power of new tools, including [Microsoft Copilot for Security](https://www.microsoft.com/security/business/ai-machine-learning/microsoft-security-copilot), to elevate defenders everywhere. ## Activity Overview ### **A principled approach to detecting and blocking threat actors** The progress of technology creates a demand for strong cybersecurity and safety measures. For example, the White House\'s Executive Order on AI requires rigorous safety testing and government supervision for AI systems that have major impacts on national and economic security or public health and safety. Our actions enhancing the safeguards of our AI models and partnering with our ecosystem on the safe creation, implementation, and use of these models align with the Executive Order\'s request for comprehensive AI safety and security standards. In line with Microsoft\'s leadership across AI and cybersecurity, today we are announcing principles shaping Microsoft\'s policy and actions mitigating the risks associated with the use of our AI tools and APIs by nation-state advanced persistent threats (APTs), advanced persistent manipulators (APMs), and cybercriminal syndicates we track. These principles include: - **Identification and action against malicious threat actors\' use:** Upon detection of the use of any Microsoft AI application programming interfaces (APIs), services, or systems by an identified malicious threat actor, including nation-state APT or APM, or the cybercrime syndicates we track, Microsoft will take appropriate action to disrupt their activities, such as disabling the accounts used, terminating services, or limiting access to resources. - **Notification to other AI service providers:** When we detect a threat actor\'s use of another service provider\'s AI, AI APIs, services, and/or systems, Microsoft will promptly notify the service provider and share relevant data. This enables the service provider to independently verify our findings and take action in accordance with their own policies. - **Collaboration with other stakeholders:** Microsoft will collaborate with other stakeholders to regularly exchange information a | Ransomware Malware Tool Vulnerability Threat Studies Medical Technical | APT 28 ChatGPT APT 4 | ★★ | |
| 2023-09-27 12:51:29 | Les lacunes de sécurité et de confidentialité SMS montrent clairement que les utilisateurs ont besoin d'une mise à niveau de messagerie SMS Security & Privacy Gaps Make It Clear Users Need a Messaging Upgrade (lien direct) |
Posted by Eugene Liderman and Roger Piqueras Jover
SMS texting is frozen in time.
People still use and rely on trillions of SMS texts each year to exchange messages with friends, share family photos, and copy two-factor authentication codes to access sensitive data in their bank accounts. It\'s hard to believe that at a time where technologies like AI are transforming our world, a forty-year old mobile messaging standard is still so prevalent.
Like any forty-year-old technology, SMS is antiquated compared to its modern counterparts. That\'s especially concerning when it comes to security.
The World Has Changed, But SMS Hasn\'t Changed With It
According to a recent whitepaper from Dekra, a safety certifications and testing lab, the security shortcomings of SMS can notably lead to:
SMS Interception: Attackers can intercept SMS messages by exploiting vulnerabilities in mobile carrier networks. This can allow them to read the contents of SMS messages, including sensitive information such as two-factor authentication codes, passwords, and credit card numbers due to the lack of encryption offered by SMS.
SMS Spoofing: Attackers can spoof SMS messages to launch phishing attacks to make it appear as if they are from a legitimate sender. This can be used to trick users into clicking on malicious links or revealing sensitive information. And because carrier networks have independently developed their approaches to deploying SMS texts over the years, the inability for carriers to exchange reputation signals to help identify fraudulent messages has made it tough to detect spoofed senders distributing potentially malicious messages.
These findings add to the well-established facts about SMS\' weaknesses, lack of encryption chief among them.
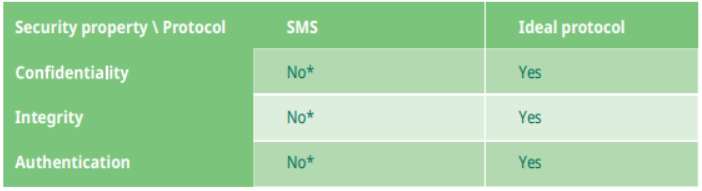
Dekra also compared SMS against a modern secure messaging protocol and found it lacked any built-in security functionality. According to Dekra, SMS users can\'t answer \'yes\' to any of the following basic security questions:
Confidentiality: Can I trust that no one else can read my SMSs?
Integrity: Can I trust that the content of the SMS that I receive is not modified?
Authentication: Can I trust the identity of the sender of the SMS that I receive?
 But this isn\'t just theoretical: cybercriminals have also caught on to the lack of security protections SMS provides and have repeatedly exploited its weakness. Both novice hackers and advanced threat actor groups (such as UNC3944 / Scattered Spider and APT41 investigated by Mandiant, part of Google Cloud) leverage the security deficiencies in SMS to launch different
But this isn\'t just theoretical: cybercriminals have also caught on to the lack of security protections SMS provides and have repeatedly exploited its weakness. Both novice hackers and advanced threat actor groups (such as UNC3944 / Scattered Spider and APT41 investigated by Mandiant, part of Google Cloud) leverage the security deficiencies in SMS to launch different |
Vulnerability Threat Studies | APT 41 | ★★★ | |
| 2023-03-30 04:40:47 | Une autre année, un autre gang nord-coréen dépassant les logiciels malveillants et crypto-vole nommé [Another year, another North Korean malware-spreading, crypto-stealing gang named] (lien direct) | mandiant identifie \\ 'modérément sophistiqué \' mais \\ 'prolifique \' apt43 comme la menace mondiale la tenue de sécurité récemment acquise de Google Cloud \\ a nommé un nouveau méchant de NorthCorée: un gang de cybercriminalité, il appelle APT43 et accuse un déchaînement de cinq ans.…
Mandiant identifies \'moderately sophisticated\' but \'prolific\' APT43 as global menace Google Cloud\'s recently acquired security outfit Mandiant has named a new nasty from North Korea: a cyber crime gang it calls APT43 and accuses of a five-year rampage.… |
Studies Prediction | APT 43 | ★★ | |
| 2021-07-20 15:00:00 | Anomali Cyber Watch: China Blamed for Microsoft Exchange Attacks, Israeli Cyber Surveillance Companies Help Oppressive Governments, and More (lien direct) | The various threat intelligence stories in this iteration of the Anomali Cyber Watch discuss the following topics: China, APT, Espionage, Ransomware, Targeted Campaigns, DLL Side-Loading, and Vulnerabilities. The IOCs related to these stories are attached to Anomali Cyber Watch and can be used to check your logs for potential malicious activity.
 Figure 1 - IOC Summary Charts. These charts summarize the IOCs attached to this magazine and provide a glimpse of the threats discussed.
Trending Cyber News and Threat Intelligence
UK and Allies Accuse China for a Pervasive Pattern of Hacking, Breaching Microsoft Exchange Servers
(published: July 19, 2021)
On July 19th, 2021, the US, the UK, and other global allies jointly accused China in a pattern of aggressive malicious cyber activity. First, they confirmed that Chinese state-backed actors (previously identified under the group name Hafnium) were responsible for gaining access to computer networks around the world via Microsoft Exchange servers. The attacks took place in early 2021, affecting over a quarter of a million servers worldwide. Additionally, APT31 (Judgement Panda) and APT40 (Kryptonite Panda) were attributed to Chinese Ministry of State Security (MSS), The US Department of Justice (DoJ) has indicted four APT40 members, and the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) shared indicators of compromise of the historic APT40 activity.
Analyst Comment: Network defense-in-depth and adherence to information security best practices can assist organizations in reducing the risk. Pay special attention to the patch and vulnerability management, protecting credentials, and continuing network hygiene and monitoring. When possible, enforce the principle of least privilege, use segmentation and strict access control measures for critical data. Organisations can use Anomali Match to perform real time forensic analysis for tracking such attacks.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] Drive-by Compromise - T1189 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Exploit Public-Facing Application - T1190 | [MITRE ATT&CK] External Remote Services - T1133 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Server Software Component - T1505 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Exploitation of Remote Services - T1210
Tags: Hafnium, Judgement Panda, APT31, TEMP.Jumper, APT40, Kryptonite Panda, Zirconium, Leviathan, TEMP.Periscope, Microsoft Exchange, CVE-2021-26857, CVE-2021-26855, CVE-2021-27065, CVE-2021-26858, Government, EU, UK, North America, China
NSO’s Spyware Sold to Authoritarian Regimes Used to Target Activists, Politicians and Journalists
(published: July 18, 2021)
Israeli surveillance company NSO Group supposedly sells spyware to vetted governments bodies to fight crime and terrorism. New research discovered NSO’s tools being used against non-criminal actors, pro-democracy activists and journalists investigating corruption, political opponents and government critics, diplomats, etc. In some cases, the timeline of this surveillance coincided with journalists' arrests and even murders. The main penetration tool used by NSO is malware Pegasus that targets both iPho
Figure 1 - IOC Summary Charts. These charts summarize the IOCs attached to this magazine and provide a glimpse of the threats discussed.
Trending Cyber News and Threat Intelligence
UK and Allies Accuse China for a Pervasive Pattern of Hacking, Breaching Microsoft Exchange Servers
(published: July 19, 2021)
On July 19th, 2021, the US, the UK, and other global allies jointly accused China in a pattern of aggressive malicious cyber activity. First, they confirmed that Chinese state-backed actors (previously identified under the group name Hafnium) were responsible for gaining access to computer networks around the world via Microsoft Exchange servers. The attacks took place in early 2021, affecting over a quarter of a million servers worldwide. Additionally, APT31 (Judgement Panda) and APT40 (Kryptonite Panda) were attributed to Chinese Ministry of State Security (MSS), The US Department of Justice (DoJ) has indicted four APT40 members, and the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) shared indicators of compromise of the historic APT40 activity.
Analyst Comment: Network defense-in-depth and adherence to information security best practices can assist organizations in reducing the risk. Pay special attention to the patch and vulnerability management, protecting credentials, and continuing network hygiene and monitoring. When possible, enforce the principle of least privilege, use segmentation and strict access control measures for critical data. Organisations can use Anomali Match to perform real time forensic analysis for tracking such attacks.
MITRE ATT&CK: [MITRE ATT&CK] Drive-by Compromise - T1189 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Exploit Public-Facing Application - T1190 | [MITRE ATT&CK] External Remote Services - T1133 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Server Software Component - T1505 | [MITRE ATT&CK] Exploitation of Remote Services - T1210
Tags: Hafnium, Judgement Panda, APT31, TEMP.Jumper, APT40, Kryptonite Panda, Zirconium, Leviathan, TEMP.Periscope, Microsoft Exchange, CVE-2021-26857, CVE-2021-26855, CVE-2021-27065, CVE-2021-26858, Government, EU, UK, North America, China
NSO’s Spyware Sold to Authoritarian Regimes Used to Target Activists, Politicians and Journalists
(published: July 18, 2021)
Israeli surveillance company NSO Group supposedly sells spyware to vetted governments bodies to fight crime and terrorism. New research discovered NSO’s tools being used against non-criminal actors, pro-democracy activists and journalists investigating corruption, political opponents and government critics, diplomats, etc. In some cases, the timeline of this surveillance coincided with journalists' arrests and even murders. The main penetration tool used by NSO is malware Pegasus that targets both iPho |
Ransomware Malware Tool Vulnerability Threat Studies Guideline Industrial | APT 41 APT 40 APT 28 APT 31 |
1
We have: 4 articles.
We have: 4 articles.
To see everything:
Our RSS (filtrered)
